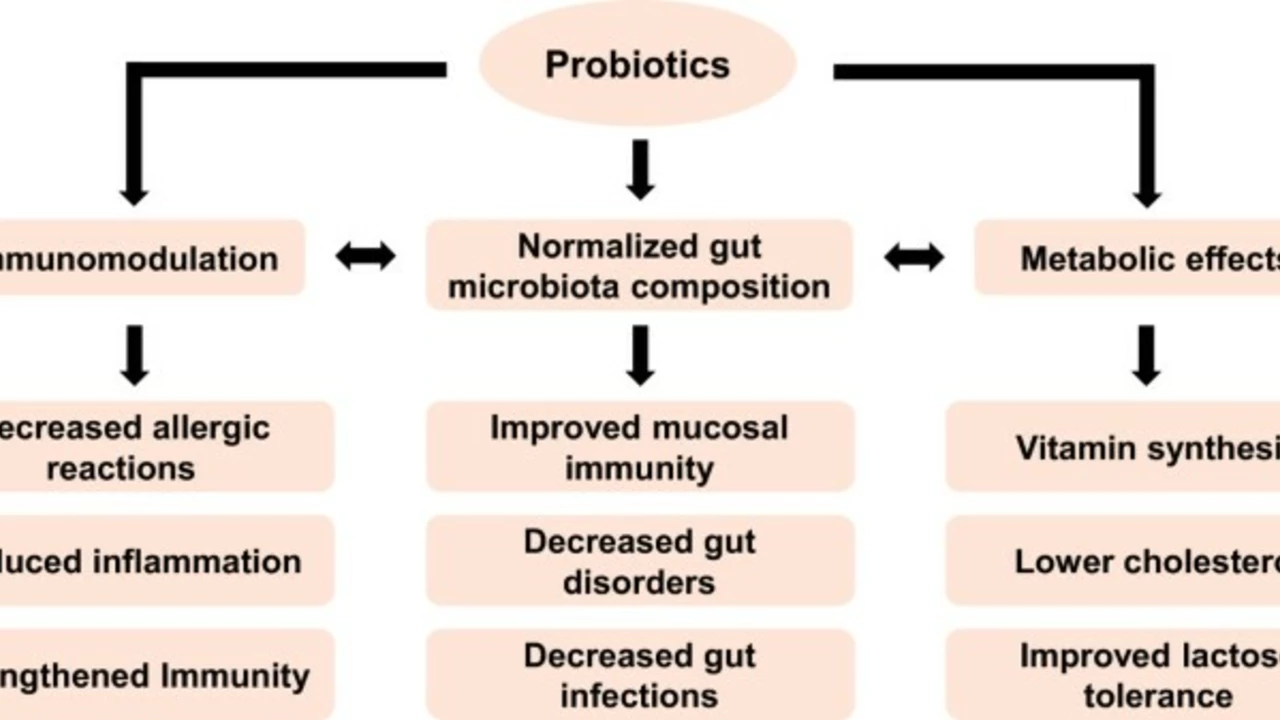
Understanding Probiotics and Their Importance
Before we dive into the role of probiotics in preventing infections, it's essential to understand what probiotics are and why they are important. Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for our health, particularly the digestive system. Our bodies are full of bacteria, both good and bad. However, probiotics are often called "good" or "friendly" bacteria because they help keep our gut healthy. They can be found in certain foods and supplements. We usually think of bacteria as something harmful, but our bodies need these beneficial bacteria to function properly.
Types of Probiotic Bacteria
There are many different types of probiotic bacteria that are beneficial for our health. The most common types are Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Lactobacillus is the most common probiotic and is often found in yogurt and other fermented foods. This type can help with diarrhea and may help people who can't digest lactose, the sugar in milk. On the other hand, Bifidobacterium can be found in some dairy products and can ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other conditions.
Probiotics and the Immune System
One of the crucial roles of probiotics is supporting the immune system. A significant portion of the immune system is actually located in the gut. Hence, having a healthy gut flora can help enhance immune responses and prevent infections. Probiotics can stimulate the body's natural defense mechanisms, making it harder for harmful pathogens to take hold. They can also help regulate inflammation, which is often a response to infection.
Probiotics in Preventing Gastrointestinal Infections
Probiotics play a crucial role in preventing gastrointestinal infections. They help maintain a healthy balance of gut flora by outcompeting harmful bacteria for nutrients and attachment sites on the gut wall. This makes it difficult for harmful bacteria to colonize and cause infections. By producing substances that inhibit harmful bacteria's growth, probiotics can further protect against gastrointestinal infections.
Probiotics and Respiratory Infections
Research has shown that probiotics can also help prevent respiratory infections. They can enhance the body's immune response to respiratory viruses, reducing the incidence and duration of infections. Probiotics can also reduce the severity of respiratory infections by modulating the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation, which can cause tissue damage.
Probiotics and Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are another area where probiotics have shown potential. Some strains of probiotics can inhibit the growth of uropathogenic bacteria, preventing them from adhering to the urinary tract walls and causing infections. While more research is needed in this area, preliminary findings are promising.
Probiotics and Skin Infections
Probiotics have also been linked to the prevention of skin infections. Some probiotics can produce antimicrobial substances that inhibit the growth of harmful skin bacteria. They can also enhance the skin's barrier function, preventing harmful bacteria from penetrating the skin and causing infections.
Choosing the Right Probiotic
With so many different types of probiotics available, choosing the right one can be confusing. The best probiotic for you depends on your health needs. Different strains of probiotics have different effects, so it's important to choose a product that contains the right strains for the health benefit you want. It's also essential to look at the number of live organisms per dose, as this can affect the product's effectiveness.
Conclusion: Probiotics and Infection Prevention
In conclusion, probiotics play an essential role in preventing infections. They support the immune system, prevent harmful bacteria from colonizing the gut, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin, and can even produce substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. While more research is needed in some areas, the evidence so far suggests that probiotics are a valuable tool in the fight against infections.

8 Comments
Prakash pawarJuly 17, 2023 AT 23:42
Probiotics are basically the yoga instructors of your gut
They don't just chill you out they rewire your entire inner ecosystem
You think antibiotics are the solution but nah bro they're the bulldozer
Probiotics are the gentle gardener replanting the lawn after the storm
Modern medicine forgets this but evolution didn't
We coevolved with these microbes for millions of years
Not some lab-made chemical you swallow like a vitamin pill
It's about harmony not eradication
And yeah I know Big Pharma doesn't profit from yogurt
But maybe that's the point
MOLLY SURNOJuly 19, 2023 AT 01:04
Thank you for sharing this well-researched overview. I appreciate how clearly the connection between gut health and systemic immunity is outlined. As someone who works in healthcare, I’ve seen patients benefit significantly from targeted probiotic use-especially after prolonged antibiotic courses. It’s encouraging to see the science catching up to what many have observed anecdotally for years.
Alex HundertJuly 20, 2023 AT 20:59
Let’s be real-probiotics aren’t magic. Most over-the-counter supplements have maybe 1% survival rate past stomach acid. The real game-changer is fermented foods. Kimchi, kefir, sauerkraut-those have live cultures that actually make it through. Supplements are just a placebo with a fancy label. If you want results, eat the food, not the pill.
Emily KiddJuly 21, 2023 AT 08:07
omg yes i’ve been taking lactobacillus for my iBS and it’s been a game changer
also my kid stopped getting ear infections after we started giving him the chewable ones
idk if it’s science or placebo but i’ll take it
also side note: the brand i use always has like 3 typos on the bottle but it works so i don’t care
Justin CheahJuly 22, 2023 AT 10:23
They’re not trying to tell you the truth about probiotics because the CDC and WHO are in bed with Big Pharma who makes billions off antibiotics and antivirals
Probiotics are a $20 billion industry that’s been suppressed since the 70s because if people could prevent infections naturally with yogurt then why would you need a $3000 hospital bill every time you sneeze
They don’t want you to know that your gut flora can outcompete MRSA
They don’t want you to know that a 1998 NIH study showed probiotics reduced ICU infections by 47%
They bury it under peer-reviewed jargon and call it ‘inconclusive’
But the data’s there if you dig past the corporate-funded studies
It’s not conspiracy it’s capitalism
caiden gilbertJuly 22, 2023 AT 18:19
It’s wild how something so tiny-bacteria you can’t even see-can be the quiet architect of your whole immune symphony
Like your gut is a coral reef and probiotics are the clownfish and sea anemones keeping the balance
When you wipe it out with antibiotics, it’s not just a reset-it’s a landslide
And yet we treat it like a broken pipe we just need to patch
Not a living, breathing, ancient ecosystem we’re lucky to coexist with
Maybe we should stop trying to control it and start learning how to listen
phenter mineJuly 23, 2023 AT 12:59
i just wanted to say i’ve been using this probiotic for my skin and it totally helped with my acne
also my digestion is way better
but i think i bought the wrong one cause the bottle says ‘lactobacullus’ not ‘lactobacillus’
but it still works so idk
maybe the typo made it more powerful
Aditya SinghJuly 24, 2023 AT 06:54
Probiotics are a red herring. The real issue is microbiome dysbiosis induced by glyphosate exposure and modern dietary fructose overload. You can’t restore gut flora with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG if your enteric nervous system is chronically inflamed due to lectin-mediated zonulin upregulation. The entire paradigm is reductionist. What we need is fecal microbiota transplantation protocols calibrated via metagenomic sequencing and personalized phage therapy. Probiotic supplements are the placebo of the 21st century wellness industrial complex.