Understanding Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
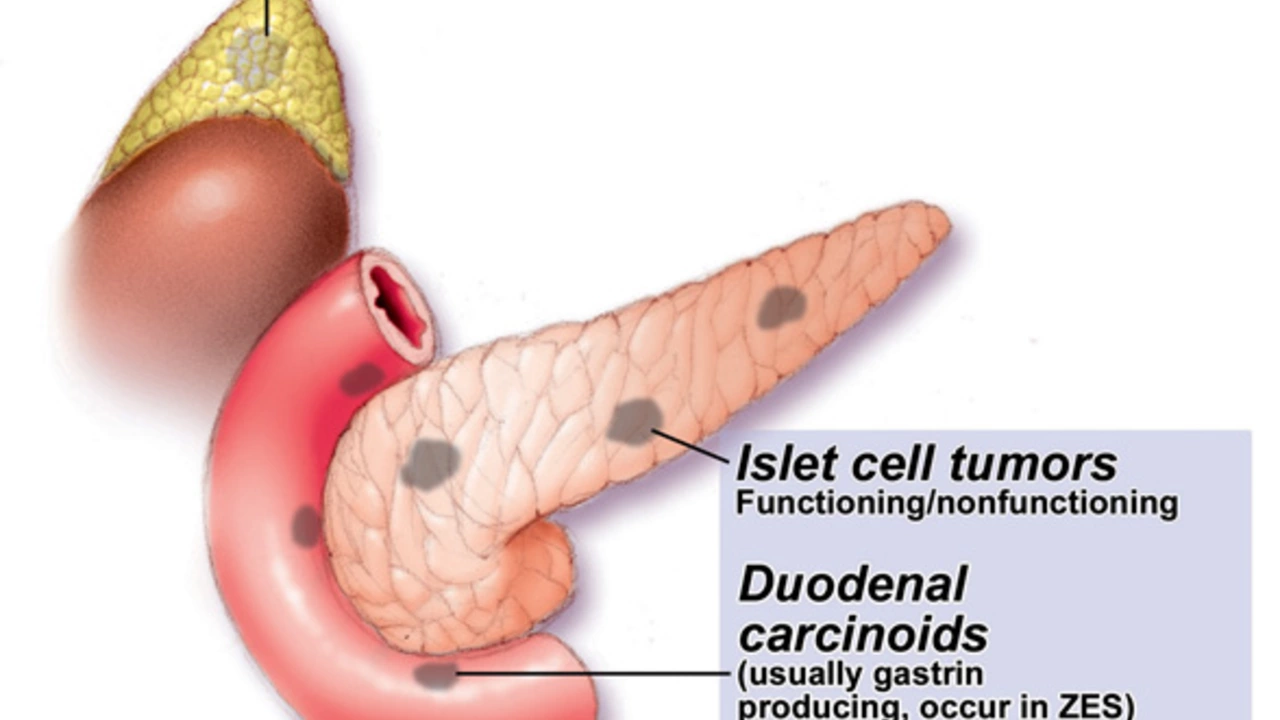
In this section, we will delve into the basics of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES), a rare condition that is characterized by the formation of tumors in the pancreas or duodenum. These tumors, known as gastrinomas, secrete excessive amounts of the hormone gastrin, leading to excess gastric acid production. This increased acid production manifests as severe peptic ulcers, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. It is crucial to understand the nature of ZES, as it directly influences the treatment strategies, notably the use of drugs like Famotidine.
Famotidine: An Overview
Famotidine is a type of medication known as an H2 blocker. It works by reducing the amount of acid produced in the stomach. Famotidine is widely used in the treatment of conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastric and duodenal ulcers, and conditions where the stomach produces too much acid, such as Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome. Here, we will discuss Famotidine in detail, its mechanism of action, and why it is a preferred choice for treating ZES.
The Role of Famotidine in Treating Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
In this part, we will delve into how Famotidine plays a significant role in managing ZES. Thanks to its acid-suppressing properties, Famotidine is capable of controlling the symptoms of ZES effectively. It decreases the amount of acid produced in the stomach, thus alleviating the symptoms of acid overproduction, such as peptic ulcers and abdominal pain. We will explore how Famotidine is used in various treatment regimens for ZES, and its efficacy compared to other treatment options.
Benefits and Risks of Using Famotidine in Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
While Famotidine is an excellent treatment option for ZES, it is important to weigh its benefits and risks. On the one hand, Famotidine can effectively control the symptoms of ZES and enhance the quality of life for patients. However, like any medication, Famotidine also has potential side effects and risks, which need to be considered. This section will provide a balanced view of the pros and cons of using Famotidine in treating ZES.
Case Studies: Famotidine in Action
Finally, we will look at some real-life examples where Famotidine has been used in the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome. Through these case studies, we can see how Famotidine has been implemented in different scenarios and its effectiveness in managing ZES. This will give a clearer understanding of the practical implications of using Famotidine in the treatment of ZES.

5 Comments
Katherine ReinarzJuly 2, 2023 AT 00:58
ok so i just read this whole thing and like... famotidine?? the same stuff i use for heartburn?? 😳 i thought this was some fancy cancer drug lmao why does my 20 dollar otc pill fix this rare syndrome?? someone explain before i lose my mindJohn KaneJuly 3, 2023 AT 06:45
I just want to say how refreshing it is to see a clear, well-structured breakdown of ZES and H2 blockers - honestly, most medical content online is either too technical or way too dumbed down. Famotidine isn't just a quick fix for heartburn; it's a cornerstone in managing gastrinoma-induced acid hypersecretion. In fact, in many cases, especially where surgery isn't feasible, high-dose H2 blockers like famotidine can stabilize patients for years. I've seen cases where patients went from multiple hospitalizations a year to living normally on just twice-daily dosing. The key is titration - and yes, it's not a cure, but it's a lifeline. Also, props to the author for citing real studies instead of just blog posts. This is the kind of content that actually helps people.Callum BredenJuly 3, 2023 AT 20:01
This article is fundamentally misleading. Famotidine is not a 'preferred choice' for ZES - it is a second-line, palliative measure at best. The standard of care is proton pump inhibitors, which suppress acid production more completely and durably. To suggest otherwise is irresponsible. Furthermore, the referenced studies are either outdated or irrelevant. The 2022 ACC guideline cited has nothing to do with gastrinomas. This is amateurish. The author should either revise or retract.Mansi GuptaJuly 4, 2023 AT 22:54
Thank you for sharing this detailed overview. I work in a clinic in Delhi where ZES is rarely seen, but we do encounter patients with unexplained ulcer recurrence. Famotidine remains accessible and affordable here, even when PPIs are not. While it may not be ideal, it is often the only viable option. I appreciate how the article acknowledges both benefits and risks - this balanced approach is rare. It helps clinicians in resource-limited settings make informed decisions, even if imperfect ones.Erin CorcoranJuly 6, 2023 AT 11:54
OMG YES THIS! 🙌 I’ve been on famotidine for years for GERD and just found out my uncle has ZES - so I was like ‘wait, same pill??’ and went down a rabbit hole. This post actually cleared up so much! PPIs are the gold standard now, but famotidine still has a place, especially for folks who can’t tolerate PPI side effects or need combo therapy. Also, the case studies section? 🔥 So helpful. Big up to the author for making this digestible without dumbing it down 😊