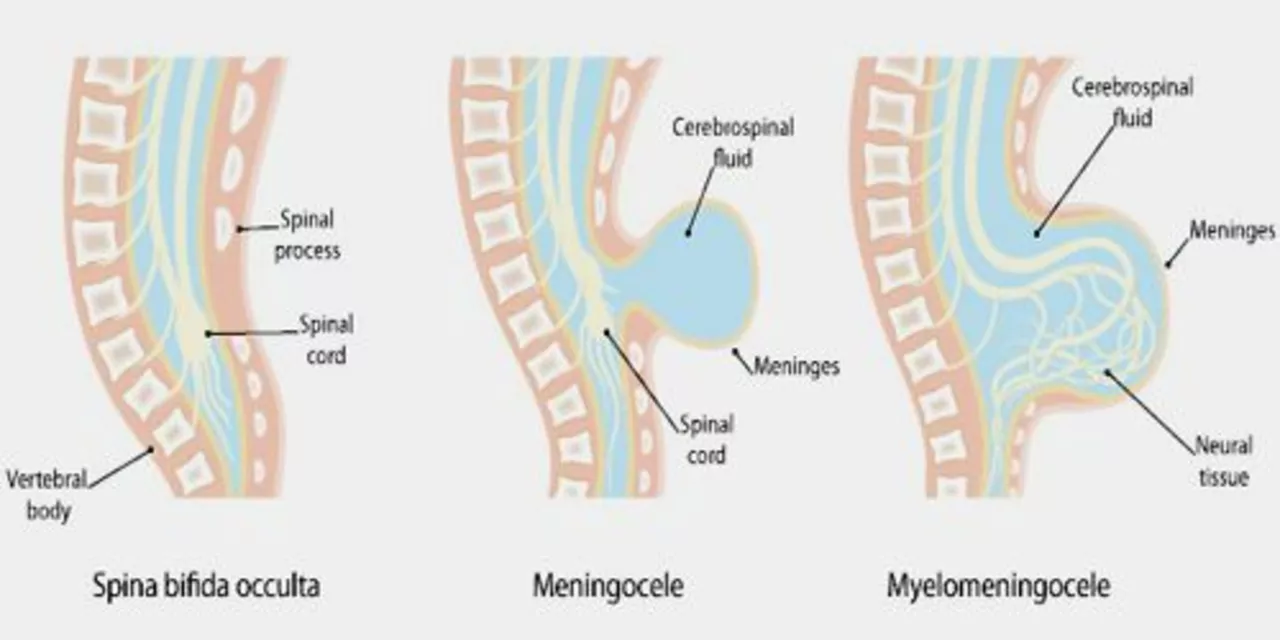
Understanding Spina Bifida
Before diving into the connection between spina bifida and mental health challenges, it's important to understand what spina bifida is. Spina bifida is a birth defect that occurs when the spine and spinal cord don't form properly. This can lead to various physical and neurological complications, depending on the severity of the condition. There are three main types of spina bifida: spina bifida occulta, meningocele, and myelomeningocele. Each type comes with its own set of challenges, but all can have an impact on a person's mental health.
Physical Challenges and Their Impact on Mental Health
Individuals with spina bifida often face numerous physical challenges, such as limited mobility, bladder and bowel issues, and chronic pain. These challenges can have a profound impact on mental health, as they can lead to feelings of isolation, frustration, and low self-esteem. Furthermore, the constant need for medical care and assistance can place a heavy emotional burden on both the individuals with spina bifida and their families, leading to increased stress and anxiety.
Cognitive and Learning Difficulties
Many people with spina bifida also experience cognitive and learning difficulties, which can contribute to mental health challenges. These difficulties can range from mild to severe, and may include problems with attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. As a result, individuals with spina bifida may struggle in school or work settings, leading to feelings of inadequacy and frustration. This can exacerbate existing mental health issues or contribute to the development of new ones, such as depression or anxiety.
Social Challenges and Stigma
Another factor that can affect the mental health of individuals with spina bifida is the social challenges and stigma they may face. Due to their physical limitations and differences, they may encounter discrimination, bullying, or social exclusion. This can lead to feelings of loneliness, rejection, and low self-worth, which can contribute to the development of mental health issues like depression and anxiety. It's important for individuals with spina bifida and their families to be aware of these challenges and to seek support when needed.
Depression and Anxiety
As mentioned earlier, depression and anxiety are common mental health challenges faced by individuals with spina bifida. The physical, cognitive, and social challenges associated with the condition can all contribute to the development of these mental health disorders. It's important for individuals with spina bifida, their families, and healthcare providers to recognize the signs of depression and anxiety and to seek appropriate treatment and support.
Building Resilience and Coping Skills
One way to help individuals with spina bifida overcome mental health challenges is by building resilience and teaching coping skills. This can involve encouraging positive thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication. Additionally, fostering a strong support system, including family, friends, and healthcare providers, can be crucial in helping individuals with spina bifida manage their mental health.
Access to Mental Health Services
Access to mental health services is vital for individuals with spina bifida who are experiencing mental health challenges. This can include therapy, counseling, and medication management. It's important for healthcare providers and families to work together to ensure that these services are accessible and tailored to the unique needs of individuals with spina bifida.
The Role of Family and Caregivers
Family members and caregivers play a crucial role in supporting the mental health of individuals with spina bifida. By providing emotional support, encouragement, and assistance with daily tasks, families and caregivers can help alleviate some of the stress and anxiety associated with living with the condition. It's also important for family members and caregivers to seek support for themselves, as caring for someone with spina bifida can be emotionally challenging.
Conclusion
Living with spina bifida can present many challenges, including those related to mental health. By understanding the connection between spina bifida and mental health challenges, individuals, families, and healthcare providers can work together to address them and improve overall quality of life. Key strategies include building resilience and coping skills, ensuring access to mental health services, and fostering strong support systems for both individuals with spina bifida and their families.

9 Comments
Michael LynchMay 16, 2023 AT 07:51
I've seen this play out with a cousin of mine. Spina bifida doesn't just affect the body-it reshapes how you see yourself in the world. The quiet moments of frustration, the way people stare or look away... it adds up. Not everyone talks about it, but it's there.caroline howardMay 16, 2023 AT 07:56
Oh wow, so now we're giving out gold stars for noticing that chronic pain makes you sad? Groundbreaking. Maybe next time someone should write an article titled 'Water is wet and breathing is hard when your lungs are broken.'Gurupriya DuttaMay 16, 2023 AT 18:10
I work with kids who have myelomeningocele. What’s rarely discussed is how much of their mental health struggle comes from being treated like a project instead of a person. The therapists mean well, but sometimes the interventions feel like checklists, not connection.Austin LevineMay 17, 2023 AT 08:20
This is real.Rika NokashiMay 17, 2023 AT 18:15
In India, we don't even have the infrastructure to diagnose spina bifida properly in rural areas-let alone mental health support. And yet, people still manage to raise their children with dignity. It's not about the system-it's about the spirit. You Westerners think therapy fixes everything, but resilience isn't prescribed-it's practiced.Keith BloomMay 18, 2023 AT 01:30
i mean like… i know ppl with sb and they’re cool but also like… why do they always seem so… sad? is it the chair? the catheters? or just… life? idk man. maybe they just need to get out more. or get a dog. dogs fix everything. right? 🤷♂️Andrea SwickMay 18, 2023 AT 09:17
I think the biggest gap isn’t access to services-it’s access to normalcy. Kids with spina bifida aren’t asking for pity or special treatment. They just want to be the kid who forgets their homework, gets teased for their shoes, or stays up too late playing video games. When we stop framing them as 'challenges' and start seeing them as people, the mental health stuff starts to heal on its own.Amelia WigtonMay 18, 2023 AT 11:14
The neuroplasticity implications are profound. When cortical reorganization occurs secondary to altered proprioceptive feedback due to spinal cord malformation, the limbic system’s regulatory pathways become dysregulated, leading to elevated cortisol levels and diminished serotonin uptake-this is not merely 'anxiety,' it's a neurobiological cascade requiring multimodal intervention including CBT, pharmacotherapy, and somatosensory integration therapy.Don MooreMay 18, 2023 AT 21:30
Thank you for sharing this thoughtful overview. I appreciate the emphasis on systemic support and caregiver well-being. As a healthcare professional, I’ve witnessed how even small acts-like consistent follow-ups or validating a patient’s emotional experience-can significantly reduce feelings of isolation. The data supports this. Compassion is not optional-it’s clinical.